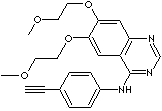
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
183319-69-9 (hydrochloride)
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white to off-white powder
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Types of chemotherapy drug;
- Alkylating agents
- Angiogenesis Inhibitors
- Anti-metabolites
- Anti-mitotics
- Aromatase inhibitors
- Biologic response modifiers
- Differentiating agents
- Hormonal therapies
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Platinum derivatives
- Signaling inhibitors
- Topoisomerase inhibitors
Both erlotinib and gefitinib have structural motif aminoquinazoline. They functions as a specific inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase. Imatinib, a derivative of 2-phenylaminopyrimidine derivative, also act as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. These drugs are called "signaling inhibitors" which kill cancer cells by attacking specific pathways and processes vital to the cancer cells' survival and growth to reduce side effects and increasing effectiveness. Tumors can grow only if they form new blood vessels to provide nutrients and oxygen. Some drugs can block blood vessel formation to cancer cells or the master signaling pathways that control cell growth. EGFR tyrosine kinase is overexpressed and mutated in various forms of cancers. Gefitinib or erlotinib bind to the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in a reversible fashion in their intracellular structure and inhibits EGFR tyrosine kinase, resulting in the signal is stop by inhibiting the ATP, autophosphorylation.
Angiogenesis inhibitors or anti-angiogenic agents include bevacizumab interfere with the pro-angiogenic action of growth factors such as basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF/FGF-2) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) that stimulates new blood vessel formation, resulting in stopping the growth of new blood vessels. Angiogenesis Inhibitors include;
Enzyme inhibitors are molecules that combine with an enzymes in such a manner as to block the enzyme's active site and to prevent the catalytic reaction, and therefore kill a pathogen or correct a metabolic imbalance. Many enzyme inhibitors are used in the field of chemotherapy, metabolic control in pharmaceuticals as well as in the field of herbicides and pesticides. Protein kinase inhibitor is a type of enzyme inhibitor which specifically blocks the action of protein kinase. Many of protein kinase inhibitors such as imatinib and dasatinib used in the treatment of cancer are tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Protein Kinase Inhibitors include;
APPEARANCE
white to off-white powder
IDENTIFICATION
to pass
ASSAY
99.0%
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
0.2% max
ISOMER
0.3% max